par1 <- as.numeric(par1)
par2 <- as.numeric(par2)
par3 <- as.numeric(par3)
par4 <- as.numeric(par4)
par5 <- as.numeric(par5)
(z <- abs(qnorm((1-par3)/2)) + abs(qnorm(1-par5)))
(z1 <- abs(qnorm(1-par3)) + abs(qnorm(1-par5)))
dum <- z*z * par4*(1-par4)
dum1 <- z1*z1 * par4*(1-par4)
par22 <- par2*par2
npop <- array(NA, 200)
ppop <- array(NA, 200)
for (i in 1:200)
{
ppop[i] <- i * 100
npop[i] <- ppop[i] * dum / (dum + (ppop[i]-1)*par22)
}
bitmap(file='pic1.png')
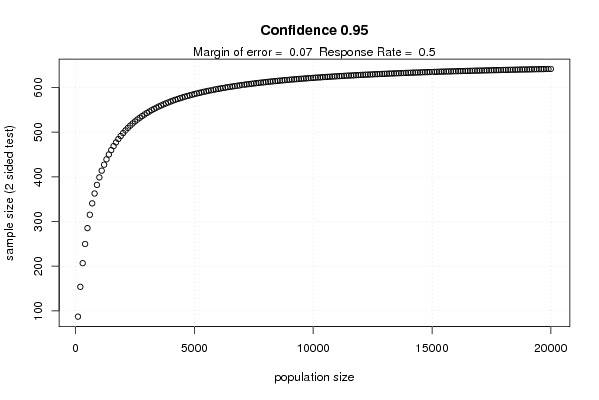
plot(ppop,npop, xlab='population size', ylab='sample size (2 sided test)', main = paste('Confidence',par3))
dumtext <- paste('Margin of error = ',par2)
dumtext <- paste(dumtext,' Response Rate = ')
dumtext <- paste(dumtext, par4)
mtext(dumtext)
grid()
dev.off()
(n <- par1 * dum / (dum + (par1-1)*par22))
(n1 <- par1 * dum1 / (dum1 + (par1-1)*par22))
load(file='createtable')
a<-table.start()
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size',2,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Population Size',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par1)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Margin of Error',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Confidence',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par3)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Power',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par5)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Response Distribution (Proportion)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par4)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'z(alpha/2) + z(beta)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,z)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'z(alpha) + z(beta)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,z1)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size (2 sided test)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,n)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size (1 sided test)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,n1)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.end(a)
table.save(a,file='mytable.tab')
(n <- dum / par22)
(n1 <- dum1 / par22)
a<-table.start()
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size (infinite population)',2,TRUE)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Population Size',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,'infinite')
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Margin of Error',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par2)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Confidence',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par3)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Power',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par5)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Response Distribution (Proportion)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,par4)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'z(alpha/2) + z(beta)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,z)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'z(alpha) + z(beta)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,z1)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size (2 sided test)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,n)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.row.start(a)
a<-table.element(a,'Minimum Sample Size (1 sided test)',header=TRUE)
a<-table.element(a,n1)
a<-table.row.end(a)
a<-table.end(a)
table.save(a,file='mytable.tab')
|